Last updated on December 27th, 2024 at 05:20 pm
The ESR full form is the Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate. The meaning of ESR in medical terms is the rate at which erythrocytes, commonly known as red blood cells, settle in a vertical tube over a specific period. It is a fundamental diagnostic tool utilized in the medical field to gauge the presence and severity of inflammation within the body.
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate elucidates the underlying principle of the test. The process involves observing the gradual sedimentation of red blood cells within a tube. The rate at which these cells descend is measured in millimetres per hour (mm/hr). This metric serves as an indirect marker for the level of inflammation present in the body.
Meaning of ESR in Medical Terms
The meaning of ESR in medical terms takes on a crucial role. Elevated ESR values often correlate with higher levels of inflammation. However, it is important to emphasize that the ESR test does not pinpoint the exact cause or location of the inflammation. Instead, it provides a general indication of its presence and severity. Various conditions, such as infections, autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammatory disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus), and certain cancers, can lead to elevated ESR levels.
When contemplating “what does ESR stand for in medical terms,” it’s crucial to recognize its role alongside other diagnostic tools. One such tool is the C-reactive protein (CRP) test, which measures a specific protein that increases during inflammation. ESR and CRP tests are often used in conjunction to provide a more comprehensive understanding of inflammatory processes within the body.
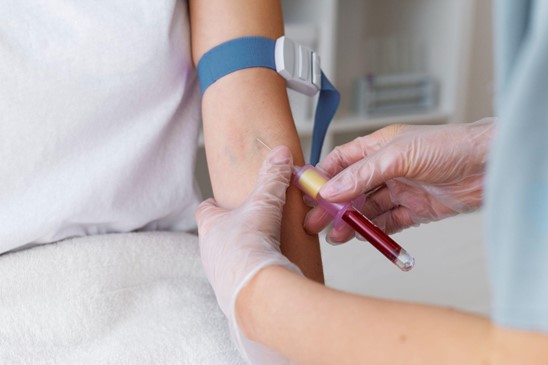
How Does ESR Work And Its Significance
Here’s how the ESR test works and what it signifies:
Test Procedure: During the test, a small amount of blood is drawn from the patient’s vein, usually from the arm. The blood is then placed in a narrow, vertical tube, where it is allowed to stand undisturbed for a certain amount of time, usually an hour. During this time, red blood cells (erythrocytes) gradually settle to the bottom of the tube due to their weight.
Sedimentation Process: Inflammation can cause certain proteins, particularly fibrinogen and other acute-phase reactants, to be released into the bloodstream. These proteins can cause the red blood cells to clump together and become heavier, leading to a faster sedimentation rate. The rate at which the red blood cells settle is measured in millimetres per hour (mm/hr).
Interpretation: A higher ESR value typically indicates a greater degree of inflammation in the body. However, it is important to note that the test doesn’t provide specific information about the cause or location of the inflammation. Various conditions can lead to elevated ESR levels, including infections, autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammatory diseases (like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus), and even some types of cancer. Conversely, a normal ESR doesn’t necessarily rule out the presence of an underlying health issue.
Read: What is Generic Medicine?
Limitations: ESR has some limitations as a diagnostic tool. It is a non-specific test, meaning that it can be elevated for a wide range of reasons. Additionally, ESR values can be influenced by factors such as age, gender, and certain medications. Therefore, ESR results are often interpreted in conjunction with other clinical and laboratory findings.
Comparison with Other Tests: The C-reactive protein (CRP) test is another commonly used test that assesses inflammation. While ESR measures the rate of red blood cell sedimentation, CRP measures a specific protein that increases in response to inflammation. Both ESR and CRP tests can provide valuable information about the presence and degree of inflammation, and healthcare providers often use them together to get a more complete picture.
Conclusion:
In summary, the ESR test is a simple and cost-effective tool that helps healthcare professionals evaluate the presence of inflammation in the body. While it doesn’t provide a definitive diagnosis, it can provide valuable information that guides further medical investigations and treatment decisions.
> Consult a doctor and Order Medicine Online
FAQs On ESR in medical terms?
Q1: What is ESR in medical terms?
ESR stands for “Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate” in medical terminology. It refers to the rate at which red blood cells settle at the bottom of a vertical tube over a specific period, usually measured in millimetres per hour (mm/hr).
Q2: What is the significance of ESR in medical diagnosis?
ESR is a non-specific indicator of inflammation in the body. An elevated ESR value suggests the presence and potential severity of inflammation, although it does not pinpoint the underlying cause. It is often used alongside other clinical and laboratory findings to aid healthcare providers in diagnosing and monitoring various conditions, such as infections, autoimmune diseases, and inflammatory disorders.
Related Links:
-
- What is a Medical Representative?
- Brain Stimulation Therapy
- Top 9 Ways to Prevent a Deadly Drug Interaction
- Are Expired Drugs Still Safe to Take?
- Why do generic and brand name drugs look different?
- Are Generic Medicines as Safe as Brand Name Drugs?
- Medical Conversions
- Genital Herpes
- What is Cognitive Behavioural Therapy?
- Medical Scribe