Last updated on June 30th, 2025 at 06:32 pm
Hemorrhagic stroke paralysis – A stroke, also known as a cerebrovascular accident, occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, causing brain cells to die due to a lack of oxygen and nutrients. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes are caused by a blockage in an artery supplying blood to the brain, while hemorrhagic strokes result from the rupture of a blood vessel in or around the brain.
Stroke paralysis occurs when the brain’s nerve cells controlling muscles are damaged or destroyed as a result of the stroke. This damage can lead to various degrees of paralysis, ranging from mild weakness to complete loss of muscle function. Paralysis severity depends on the extent of brain damage and the specific area of the brain affected.
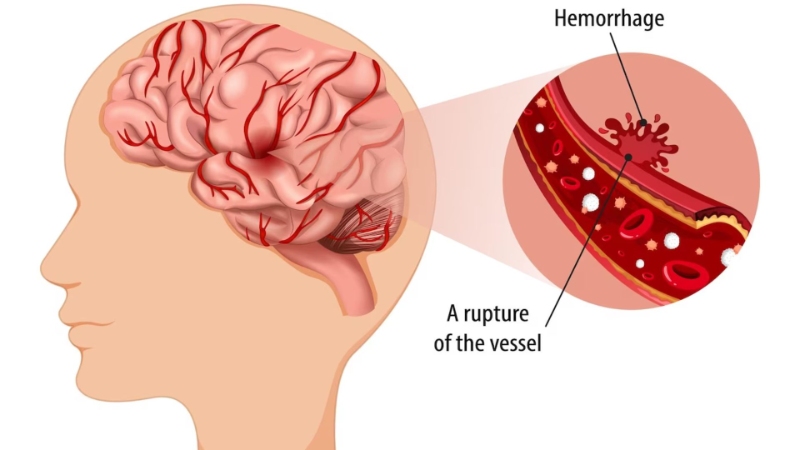
What is Hemorrhagic Stroke Paralysis?
Hemorrhagic stroke paralysis refers to the paralysis that occurs as a result of a hemorrhagic stroke. A ruptured blood vessel can damage brain cells controlling muscle movement by leaking blood into the brain or surrounding tissues. This damage can cause paralysis on one or both sides of the body, depending on its location and severity.
The paralysis experienced by an individual after a hemorrhagic stroke can be temporary or permanent. In some cases, the brain can recover and regain control over the paralyzed muscles, while in other cases, the damage may be too severe for any significant recovery to occur.
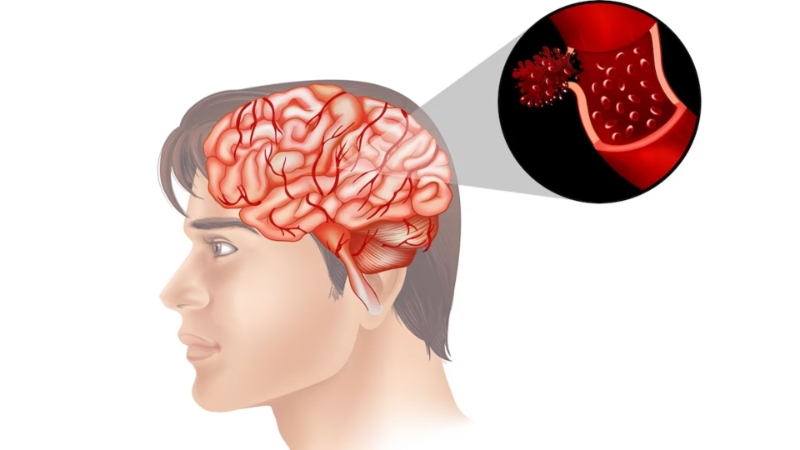
Causes of Hemorrhagic Stroke
Hemorrhagic strokes can be caused by various factors, including:
- High blood pressure: Chronic high blood pressure can weaken the walls of blood vessels, making them more susceptible to rupture and bleeding.
- Aneurysm: An aneurysm is a weakened, bulging area in a blood vessel that can rupture and cause a hemorrhagic stroke.
- Arteriovenous malformation (AVM): AVM is an abnormal tangle of blood vessels connecting arteries and veins, which can rupture and cause a hemorrhagic stroke.
- Blood vessel abnormalities: Some individuals are born with abnormalities that increase their risk of experiencing a hemorrhagic stroke.
- Blood-thinning medications: Blood-thinning medications like warfarin or aspirin increase the risk of bleeding in the brain.
Symptoms of Hemorrhagic Stroke
The symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke paralysis can vary depending on the location and severity of the brain damage. Common symptoms include:
- Sudden weakness/numbness: This can occur on one or both sides of the body, including the face, arm, or leg.
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech: Some individuals may experience slurred speech or difficulty understanding others.
- Vision problems: Hemorrhagic strokes can cause sudden vision loss, blurred vision, or double vision.
- Severe headache: A sudden, severe headache with no known cause is a common symptom of a hemorrhagic stroke.
- Loss of balance or coordination: Some individuals may experience difficulty walking, dizziness, or a sudden loss of balance.
> Consult a doctor and Order Medicine Online
Diagnoses and Treatment of Hemorrhagic Stroke
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for improving the chances of recovery and minimizing the risk of long-term complications. The diagnostic process for hemorrhagic stroke paralysis typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests such as a computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to determine the location and extent of the bleeding in the brain.
Once a hemorrhagic stroke has been diagnosed, the primary goal of treatment is to stop the bleeding and minimize brain damage. This may involve medications to lower blood pressure and prevent seizures, as well as surgical interventions to repair damaged blood vessels or remove blood clots. In some cases, a ventriculostomy may be performed to drain excess fluid from the brain and relieve pressure.
Rehabilitation is a critical component of hemorrhagic stroke treatment, as it can help individuals regain lost function and improve their quality of life. Rehabilitation may involve physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy, depending on the specific needs of the individual.
Post-Stroke Care and Support
Following a hemorrhagic stroke, individuals may require ongoing care and support to manage their symptoms and maximize their recovery. This can include regular check-ups with healthcare providers, medications to control blood pressure and prevent seizures, and support services such as home care or assisted living facilities.
Family and caregivers aid recovery with emotional support, encouragement, and daily assistance, playing crucial roles in the process. It’s essential for caregivers to educate themselves about hemorrhagic stroke paralysis and the available resources to ensure they can provide the best possible care.
Prevention
Not all hemorrhagic stroke paralysis can be prevented, but lifestyle changes can reduce the risk of some cases. These include:
- Managing blood pressure: Regular check-ups and prescribed medications can help keep blood pressure within a healthy range
- Eating a healthy diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help lower the risk of high blood pressure and other stroke risk factors.
- Exercising regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of high blood pressure, diabetes, and other stroke risk factors.
- Not smoking: Smoking increases the risk of stroke by damaging blood vessels and increasing blood pressure. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of stroke.
- Limiting alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase blood pressure and the risk of stroke. It’s essential to limit alcohol intake to moderate levels – up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
Also Read: What are Generic Medicine?
Recovery
Recovery after hemorrhagic stroke paralysis varies highly based on brain damage severity and individual’s overall health. Some improve, others remain paralyzed, needing continuous care and support.
Individuals and caregivers must maintain realistic recovery expectations and prepare for potential challenges that may arise during the process. By working closely with healthcare providers and rehabilitation specialists, individuals can maximize their chances of recovery and improve their quality of life.
Conclusion:
Hemorrhagic stroke paralysis can be a life-altering event, causing significant physical and emotional challenges for individuals and their families. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments, individuals can navigate the recovery process, enabling informed decisions by both individuals and caregivers. Additionally, by adopting healthy lifestyle habits and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can reduce their risk of experiencing a hemorrhagic stroke and improve their chances of recovery should a stroke occur.
Related Links:
- What is Sinus Headaches?
- Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cysts
- Anxiety Disorder
- What happens if we take Dolo 650 without Fever?
- Difference Between Anxiety and Depression
- Insulin Injection Site
For access to more such interesting articles on healthcare, visit Medkart today!