Last updated on May 8th, 2025 at 12:16 pm

Obesity is a chronic health condition. It is defined as the abnormal accumulation of fat that leads to several other health complications. Worldwide, obesity is considered an epidemic, with over 4.7 million deaths being recorded every year. Excessive calorie consumption can lead to obesity.
Over time, it affects the vital organs in your body and gives rise to chronic health conditions like type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart disease, kidney disease, sleep apnea, and cancer.
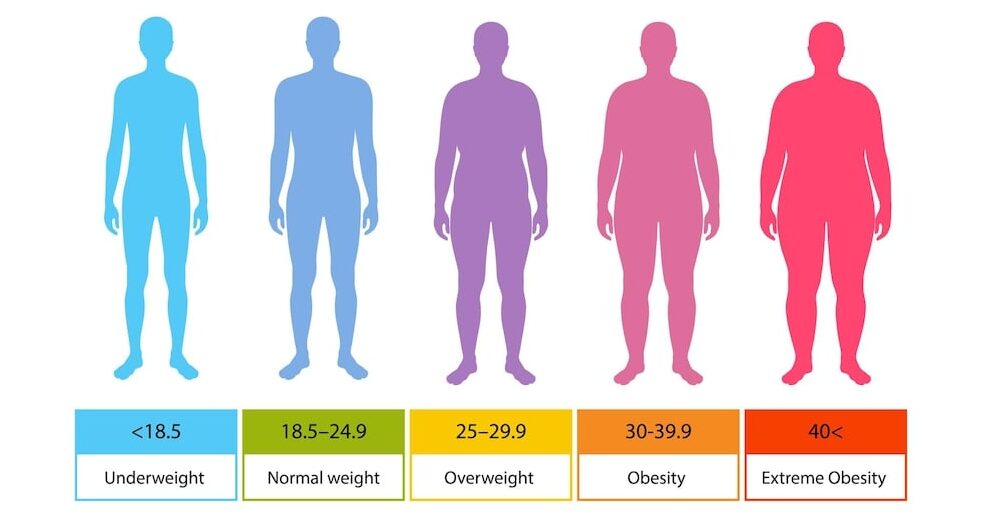
Types of Obesity (BMI Range)
Doctors measure Body Mass Index (BMI) to determine the types of obesity.
BMI = weight (kg) divided by height (meters squared)
- Optimal weight = BMI 18.5 to 24.9 kg/m2
- Overweight = BMI 25 to 29.9 kg/m2
- Obese = BMI 30 kg/m2 and above
Types of obesity based on BMI
There are three classes of obesity based on BMI. These are:
- Class 1 Obesity = BMI 30 to 35 kg/m2
- Class 2 Obesity = BMI 35 to 40 kg/m2
- Class 3 Obesity = BMI 40 kg/m2 and above
Class 3 obesity is also known as morbid or severe obesity. Three forms of obesity are based on the area of fat distribution.
Types of obesity based on the area of fat distribution
Peripheral obesity: Excessive fat accumulation in the hips, thighs and buttocks
Central obesity: Excessive fat accumulation around the abdomen. It increases the risk factors of obesity, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, kidney disease and some cancers. Combination obesity: Accumulation of excess fat in the peripheral and central regions.
Obesity types that occur due to diseases
Obesity is also classified based on its association with other diseases:
Type 1 obesity
This type of obesity is caused more commonly due to the excessive intake of calories and a lack of physical activity.
Type 2 obesity
This type of obesity is a result of diseases such as hypothyroidism (a condition characterised by an underactive thyroid), Cushing’s syndrome (a condition associated with high cortisol levels), polycystic ovary syndrome (an imbalance of female reproductive hormones) and insulinoma (a type of pancreatic tumour).
Obesity based on the size and number of fat cells
The types of obesity based on the characteristics of fat cells are:
- Hypertrophic obesity: This type of obesity occurs due to the increase in the size of adipose cells (fat cells). It usually occurs in adults.
- Hyperplastic obesity: This type of obesity occurs due to an increase in the number of fat cells. This type is predominant among children.
Complications of obesity
Different types of obesity increase the risk of several chronic diseases. These are:
- Type 2 diabetes: Excess fat makes the body resistant to insulin, which leads to high blood sugar levels or type 2 diabetes.
- Heart disease and stroke: Obesity raises blood sugar, blood pressure and cholesterol levels. It leads to narrowed or hardened arteries that block the blood flow and increase your risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Sleep apnea: Excess fat makes your airways small. This causes your breathing to stop for short periods during sleep. Low blood oxygen can cause an irregular heartbeat.
- Kidney disease: Obesity and type 2 diabetes, besides high blood pressure, directly impact your kidneys and put you at risk of kidney disease.
- Liver disease: Excess fat build-up around the liver leads to liver damage or failure.
- Gallbladder disease: Obesity increases your risk of gallstones due to high cholesterol levels in the bile.
- Osteoarthritis: Excess weight due to obesity puts pressure on your joints, like knees, hips and ankles, and causes pain, swelling and stiffness.
- Cancers: An accumulation of visceral fat around your vital organs increases your risk of developing cancer of the uterus, cervix, breast, ovary, colon, rectum, esophagus, gallbladder, kidney, liver, pancreas and prostate.
- Infertility: Different types of obesity can lead to hormonal imbalances. It disrupts the menstrual cycle and ovulation and leads to reduced fertility.
Related – Why is obesity considered as a lifestyle chronic disease? | Chronic Disease
How to Treat obesity today
The different types of obesity impact your overall health and quality of life. Consult your family physician for help with your diet and lifestyle habits to reduce your weight. Even a modest weight loss can help prevent the complications associated with the different types of obesity. For more informative articles on chronic health conditions, visit Medkart today! You can now upload your prescriptions to the website and have quality generic medicines delivered to your doorstep.
Read: What are Generic Medicines?
FAQs on Types of Obesity
Q1. What are the treatment options for morbid obesity?
A combination of physical activity, medical treatment, dietary changes, behavioral modifications and counselling is prescribed. Bariatric surgery is reserved for those who fail to achieve their weight loss goals despite several attempts.
Q2. Can fad diets help me achieve my weight loss goals?
Fad diets or crash diets impact your overall health. They cause nutritional deficiencies, dehydration, fatigue, nausea and weakness as they restrict certain food groups and nutrients. A balanced diet that includes all the food groups is a better and healthier option for losing weight.
Q3. Will obesity pose a risk during pregnancy?
Hypertension, gestational diabetes and blood clots due to obesity can cause complications during pregnancy. Obesity can also lead to preterm birth. Such babies are often born with short-term or long-term health conditions.
Related Links:
- How to get Periods immediately?
- Doctors must mention Reason while Prescribing Antibiotics
- Why Prescription by Brand Name is Dangerous?
- Generic Product Development Process
- How to Identify Generic Medicine?
- Best Acupuncture Treatment
- Tinnitus Treatment
- Best Stye Treatment
- Stomach Ulcer Treatment
- Latest Schizophrenia Treatment
- Plantar Fasciitis Treatment
- Best Pimple Treatment
