Last updated on July 11th, 2025 at 06:30 pm
 Boost Your Gut Health: A Guide To Pre And Probiotics: In the past few years, there has been a notable surge in awareness surrounding gut health within the realms of wellness and nutrition. Research has shown that a healthy gut microbiome, comprised of trillions of bacteria and other microorganisms, plays a crucial role in various aspects of our health, including digestion, immune function, mental well-being, and even weight management. One of the key ways to support a healthy gut is by incorporating prebiotics and probiotics into your diet.
Boost Your Gut Health: A Guide To Pre And Probiotics: In the past few years, there has been a notable surge in awareness surrounding gut health within the realms of wellness and nutrition. Research has shown that a healthy gut microbiome, comprised of trillions of bacteria and other microorganisms, plays a crucial role in various aspects of our health, including digestion, immune function, mental well-being, and even weight management. One of the key ways to support a healthy gut is by incorporating prebiotics and probiotics into your diet.
Understanding Prebiotics and Probiotics
- Prebiotics: Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers found in certain foods that serve as fuel for beneficial bacteria in the gut. While they remain undigested as they pass through the upper gastrointestinal tract, they reach the colon intact, where they are fermented by the gut microbiota. This fermentation process produces short-chain fatty acids, such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate, which are beneficial for gut health. Prebiotics essentially act as food for probiotics, promoting the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria in the gut. Common sources of prebiotics include fruits (e.g., bananas, apples), vegetables (e.g., onions, garlic), whole grains (e.g., oats, barley), and legumes (e.g., chickpeas, lentils). By nourishing the gut microbiome, prebiotics support digestive health, enhance immune function, and may even have positive effects on mental well-being.
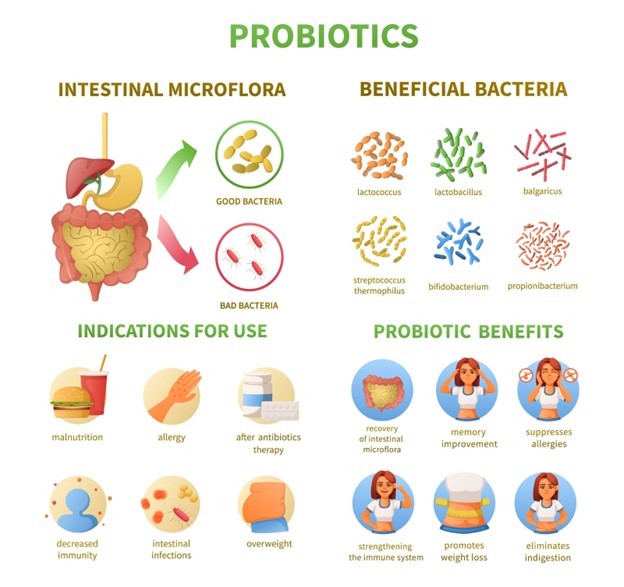
- Probiotics: Probiotics are live microorganisms, primarily bacteria and some yeasts, that confer health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. These beneficial bacteria colonize the gut and help maintain a diverse and balanced microbial environment. Probiotics can be found in certain fermented foods (e.g., yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut) as well as in supplement form. They work in various ways to support gut health, including competing with harmful bacteria for resources and adhesion sites, producing antimicrobial substances, and modulating immune responses. Probiotics have been studied for their role in improving digestion, enhancing immune function, supporting mental health, and aiding in weight management. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet or taking probiotic supplements can help optimize your gut microbiome and promote overall well-being.
Benefits of Prebiotics and Probiotics
The consumption of prebiotics and probiotics offers a multitude of benefits for overall health and well-being:
- Improved Digestive Health: Prebiotics and probiotics work synergistically to promote a healthy digestive system. Prebiotics help nourish the gut bacteria, while probiotics help maintain a balanced microbial environment, thereby aiding in digestion and reducing symptoms of digestive disorders such as bloating, gas, and constipation.
- Enhanced Immune Function: A notable fraction of the body’s immune defenses are situated within the gastrointestinal tract. By supporting a diverse and balanced gut microbiome, prebiotics and probiotics can help strengthen immune function, reducing the risk of infections and inflammatory conditions.
- Mental Health Support: Emerging research suggests a strong connection between gut health and mental well-being. The intricate gut-brain axis serves as a two-way communication pathway linking the gut and the brain, exerting profound effects on mood regulation, cognitive processes, and behavioral patterns.Consuming prebiotics and probiotics may help alleviate symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression by modulating this gut-brain connection.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy balance of gut bacteria is associated with better weight management and metabolism. Prebiotics and probiotics may help regulate appetite, reduce inflammation, and promote the breakdown of fats, contributing to a healthy body weight.
Dietary Sources of Prebiotics and Probiotics
Incorporating prebiotics and probiotics into your diet is relatively straightforward, thanks to the abundance of natural food sources:
- Prebiotic Foods:
- Chicory root
- Garlic
- Onions
- Leeks
- Asparagus
- Bananas
- Apples
- Oats
- Barley
- Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas)

- Probiotic Foods:
- Yogurt (with live active cultures)
- Kefir
- Fermented vegetables (sauerkraut, kimchi)
- Tempeh
- Miso
- Kombucha
- Pickles (naturally fermented)
- Traditional buttermilk
- Raw cheese
It’s important to note that not all fermented foods contain live probiotic cultures, so be sure to check labels for phrases like “live active cultures” or “contains probiotics.”
Supplements to Boost Your Gut Health
Supplements can be valuable additions to your regimen for boosting gut health through prebiotics and probiotics. Prebiotic supplements typically contain concentrated forms of fibers such as inulin, oligosaccharides, or fructooligosaccharides (FOS), which serve as nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria. These supplements can be particularly useful for individuals who struggle to consume sufficient prebiotic-rich foods in their diet.
Probiotic supplements such as Vizylac Capsule, on the other hand, offer specific strains of beneficial bacteria in high concentrations. They can be beneficial for those seeking targeted support for digestive issues, immune function, or overall gut health. When selecting probiotic supplements, it’s essential to choose those with strains that have been clinically studied for their efficacy and safety. Additionally, look for supplements with a diverse range of bacterial strains to support a healthy gut microbiome. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure it’s appropriate for your individual health needs.
How to Optimizing Gut Health ?
To optimize your gut health and maximize the benefits of prebiotics and probiotics, consider the following tips:
- Diversify Your Diet: Consume a wide variety of prebiotic and probiotic-rich foods to promote a diverse gut microbiome.
- Minimize Processed Foods: Processed foods high in sugar, artificial additives, and preservatives can disrupt gut health. Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods instead.
- Manage Stress: Prolonged stress has the potential to detrimentally affect the well-being of your gut. Incorporate stress-reducing practices such as mindfulness, meditation, and regular physical activity into your routine.
- Avoid Overuse of Antibiotics: Antibiotics can indiscriminately kill both harmful and beneficial bacteria in the gut. Use antibiotics only when necessary and consider taking probiotics alongside them to mitigate potential disruptions to gut flora.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how different foods and lifestyle factors affect your digestion and overall well-being. Adjust your diet and habits accordingly to support optimal gut health.
Conclusion
Incorporating prebiotics and probiotics into your diet is a proactive step towards improving your gut health and overall well-being. By nourishing the beneficial bacteria in your gut and maintaining a balanced microbial environment, you can experience digestive comfort, enhanced immunity, better mental health, and more efficient weight management. With a diverse array of dietary sources and supplements available, supporting your gut health has never been more accessible. Start small by incorporating a few prebiotic and probiotic-rich foods into your daily meals, and gradually expand your repertoire to reap the full benefits of a healthy gut microbiome. Your gut will thank you for it!
FAQs on Boost Your Gut Health: A Guide to Pre and Probiotics
1. What is pre and probiotics?
Answer: Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers found in certain foods that fuel beneficial bacteria in the gut, supporting digestion and immune function. Probiotics are live microorganisms, primarily bacteria and some yeasts, that confer health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. They colonize the gut and help maintain a diverse and balanced microbial environment, promoting overall gut health and well-being.
2. Why are prebiotics important for gut health?
Answer: Prebiotics are essential for gut health as they serve as food for beneficial bacteria in the gut microbiome. By nourishing these bacteria, prebiotics help maintain a diverse and balanced microbial environment, supporting digestion, immune function, and overall well-being.
3. Can I get enough probiotics from food alone, or do I need supplements?
Answer: While it’s possible to obtain probiotics from fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, some individuals may benefit from probiotic supplements, especially if they have specific health concerns or dietary restrictions. Supplements can provide a concentrated dose of beneficial bacteria to support gut health effectively.
4. How long does it take to notice the benefits of prebiotics and probiotics?
Answer: The timeframe for experiencing the benefits of prebiotics and probiotics can vary depending on factors such as individual gut health, diet, lifestyle, and the specific strains of bacteria consumed. While some people may notice improvements in digestion and overall well-being within a few days or weeks, it may take several weeks or even months for others to experience significant changes. Consistency is key, so aim to incorporate prebiotic and probiotic-rich foods into your diet regularly for long-term gut health benefits.
Also Read:-